Sanyo Chemical Group contributes to realizing social sustainability by offering performance chemicals that address environmental needs.
Avoided CO2 Emissions
Generally calculated as follows, avoided CO2 emission quantifies the contribution of products and services to mitigating climate change throughout society by measuring the difference in CO2 emissions between conventional and new products and services.
Formula for calculating avoided CO2 emissions:
(CO2 emissions from conventional products − CO2 emissions from new products) × quantity (e.g., sales volume, production volume, or shipment volume).
- As the formula for calculating avoided CO2 emissions includes factors such as product and service sales volume, avoided CO2 emissions are considered to be an indicator correlated with sales and a company's production capacity.
- Rules regarding calculation methods and disclosure are currently under discussion, and are mainly based on the "Guidance on Avoided Emissions" issued by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) and on initiatives by industry groups and others. However, the establishment of international standards for calculation methods is still in progress. Going forward, we will review our avoided CO2 emissions calculations in line with any changes to calculation methods that may be standardized in the future, such as when they differ from the methods we currently use or when they are revised.
Conceptual diagram of avoided CO2 emissions
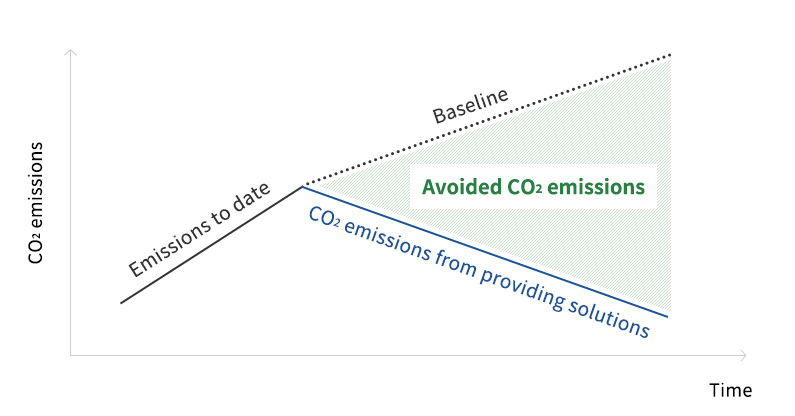
- (Source) WBCSD/Net Zero Initiative 「Guidance on Avoided Emissions: Helping business drive innovations and scale solutions towards Net Zero」(2023)
Use-Phase CO2 Reduction Strategy
We classify our main products that contribute to avoided CO2 emissions into two categories: "direct contribution " and "indirect contribution ," and calculate the impact of avoided CO2 emissions at the usage and disposal stages of a product's life cycle. Our definitions of "direct contribution " and "indirect contribution " are as follows:
- Direct contribution : Our products contributing to avoided CO2 emissions through their own performance, directly reducing CO2 emissions.
- Indirect contribution : Our products contributing to avoided CO2 emissions indirectly, by being incorporated into customers’ products or equipment that themselves reduce CO2 emissions.
Examples of Major Environmental Performance Chemicals
*Horizontally scrollable
| Category | Example products | Key areas of contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Direct contribution | ACLUBE (Lubricant additives) |
Contribution to automobile fuel efficiency |
| SANELEK (Chemicals for special electronic parts) |
Contribution to curbing capacitor overproduction by extending capacitor service life | |
| Indirect contribution | CHEMITYLEN (Chemicals for special fibers) |
Contribution to renewable energy (wind power, etc.) proliferation |
Product Life Stages Subject to Emissions Reduction
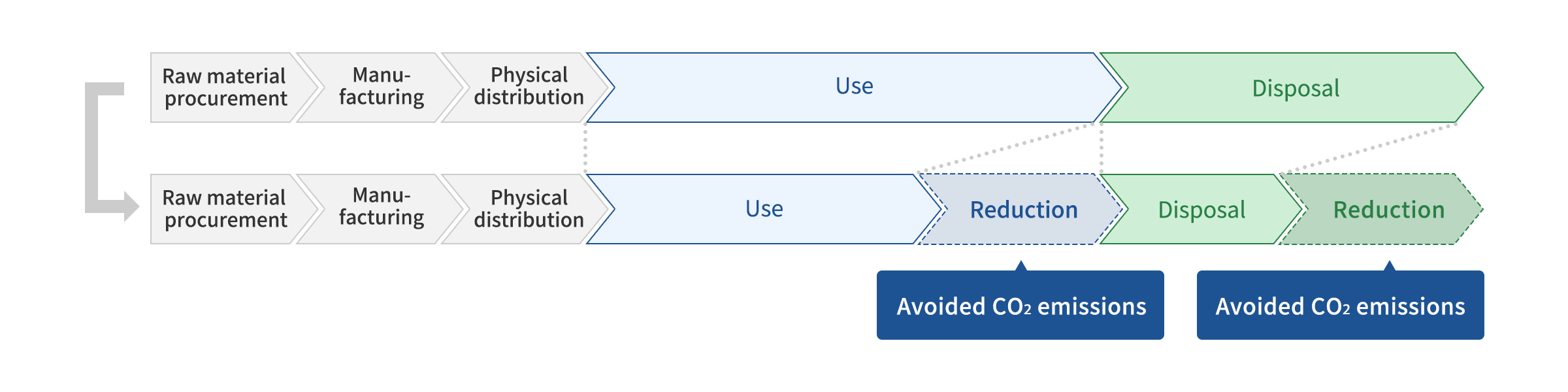
Supplementary information
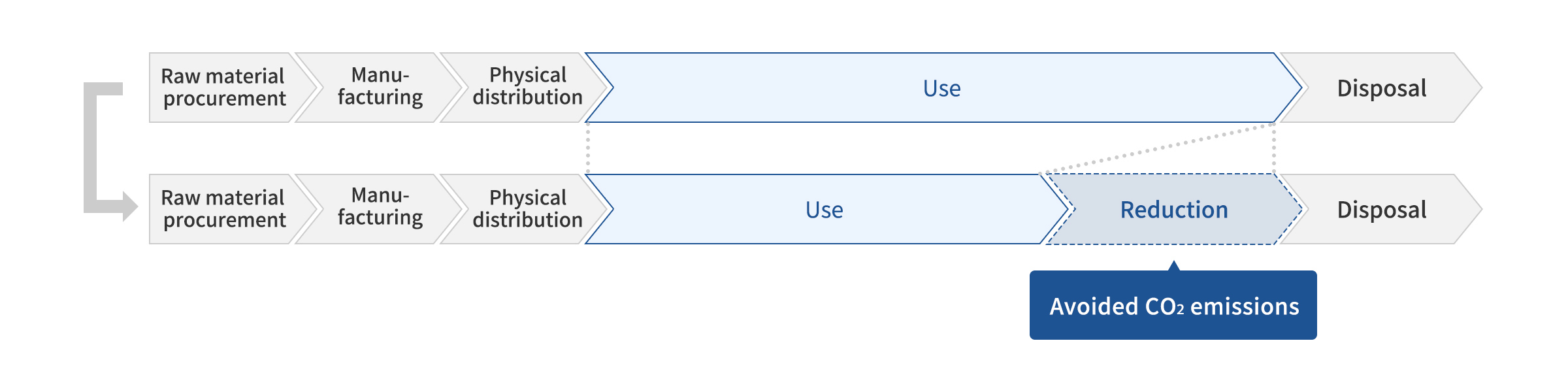
- When calculating avoided CO2 emissions , we exclude the procurement and manufacturing stages because there is little difference compared to our existing products, and calculate it based on the impact at the use and disposal stages.
- When calculating avoided CO2 emissions , we use actual or forecast values and publicly available information whenever possible. However, when such information is difficult to obtain, we base our calculations on assumptions and scenarios.
- The disclosed information, including calculation approaches and formulas, is reviewed by external experts.
Guidelines referenced
- WBCSD/Net Zero Initiative 「Guidance on Avoided Emissions: Helping business drive innovations and scale solutions towards Net Zero」(2023)
- Guidelines-Accounting For And Reporting Greenhouse Gas (GHG)Emissions Avoided Along The Value Chain, Japan Chemical Industry Association
Lubricating Oil Additives, ACLUBE Products
ACLUBE is added to lubricating oils as a viscosity index improver, which is essential for reducing friction and ensuring the smooth operation of machinery.
Since liquids generally become less viscous at high temperatures and more viscous at low temperatures, viscosity index improvers that suppress these fluctuations significantly influence the performance of lubricating oils used over a wide temperature range (approximately -30°C to 150°C).
The main component of viscosity index improvers is oil-soluble polymers that expand their molecular chains at high temperatures to prevent viscosity reduction and contract them at low temperatures to avoid viscosity increase. This enables lubricating oils to both improve fuel efficiency and protect engines.
Our ACLUBE is a viscosity index improver that primarily comprises methacrylate-based polymers. When blended appropriately with base oil, ACLUBE enables the formulation of lubricants with excellent viscosity characteristics. ACLUBE is used in a wide range of applications, including automotive engine oils and transmission fluids. It also contributes to conserving energy and reducing CO2 emissions, thereby helping to resolve energy issues and address climate change.
≫ Sanyo Chemical Products & Technologies (Japanese only)

Product Life Stages Subject to Emissions Reduction
Avoided CO2 Emissions
Calculation formula
Avoided CO2 emissions = Avoided CO2 emissions per 1 kg of product*1 × sales volume*2
-
CO2-equivalent value (18.4 -40.5 kg-CO2/kg), calculated by converting the fuel-efficiency improvement (amount of gasoline conserved) relative to vehicles using the previous-generation product.
Requirements- Conventional fuel economy: 13.13km/L (2023 Annual Report of Automobile Fuel Consumption Statistics, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism)
- Fuel consumption reduction: 0.5-1.1% (values may vary depending on application)
- Amount of this product added to lubricating oil: 12%
- Annual sales volume of applicable products (tons/year)
Calculation results
Avoided CO2 emissions (based on WBCSD Guidance) = approx. 770,000 tons CO2/year
Chemicals for Special Electronic Parts, SANELEK Products
SANELEK is a high-performance electrolyte for aluminum electrolytic capacitors. It uses a proprietary amidine compound for electrolyte to achieve high reliability and a long lifespan.
Capacitors are used in electronic control devices in automobiles and other applications to stabilize circuit operation by regulating current and voltage. They also serve as rechargeable power sources that store and release electricity. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors, which can store large amounts of electricity in a small space, are key components of electronic circuits used in many household appliances and digital products. Due to the demand for longer lifespans and lower impedance, high-performance electrolytes have become indispensable.
SANELEK achieves high electrical conductivity over a wide temperature range and excellent long-term stability at high temperatures, contributing to smaller and longer-lasting capacitors.
≫ Sanyo Chemical Products & Technologies (Japanese only)
≫ SANYO CHEMICAL MAGAZINE (Japanese only)

Product Life Stages Subject to Emissions Reduction

Avoided CO2 Emissions
Calculation formula
- Avoided CO2 emissions=
- Suppressing of capacitor overproduction by extending capacitor service life*1
× Number of capacitors produced using our products*2
× CO2 emissions during capacitor production*3
-
Mechanism for suppressing overproduction
Since SANELEK can be used in high-temperature (125°C guaranteed) capacitors, its product life is approximately four times longer than that of conventional electrolytes based on tertiary amine-derived salt used in low-temperature (105°C guaranteed) capacitors (estimated based on the 10°C doubling rule) -
Number of capacitors produced using SANELEK: 21.5 billion capacitors
(Converted and calculated based on research data from market research companies and our market information) - Database values are used
Calculation results
Avoided CO2 emissions (based on WBCSD Guidance) = approx. 130,000 t-CO2/year
Chemicals for Special Fibers, CHEMITYLEN Products
CHEMITYLEN is a chemical agent that bundles carbon fiber (CF) together for easier handling.
Carbon fiber is characterized by its strength and lightness, with a strength per unit weight about 10 times that of steel and roughly seven times more resistant to deformation. In addition to being resistant to expansion and rust, it offers many advantages that include durability against chemicals and heat and excellent X-ray permeability. It was first used on sports fields in the 1970s and has since expanded into various fields as a substitute for metal, including industrial applications in the 1990s and the aerospace and energy fields in the 2000s and onward.
However, carbon fiber is formed from individual fibers only a few micrometers in diameter, making it prone to breaking when used alone. Therefore, it is necessary to bundle thousands to tens of thousands of these fibers into thick threads, and the carbon fiber sizing agent CHEMITYLEN binds each individual carbon fiber in this process. This chemical agent enhances the strength and rigidity of carbon fiber, indirectly contributing to applications such as wind power generation equipment and lightweight transportation vehicles.
≫ Sanyo Chemical Products & Technologies

Carbon fibers (CF)

Product Life Stages Subject to Emissions Reduction
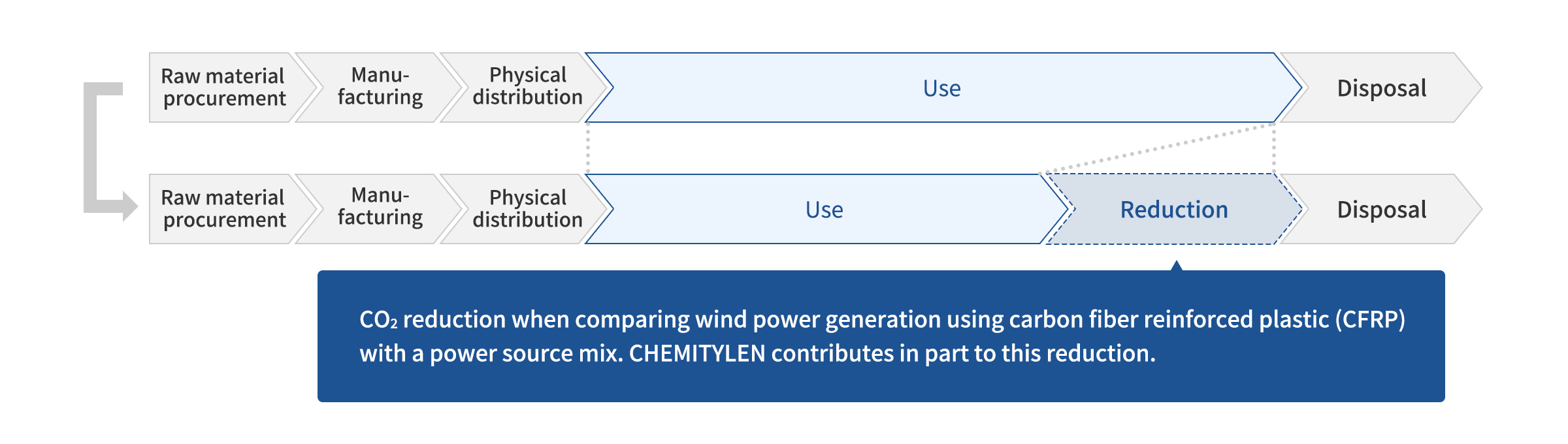
Avoided CO2 Emissions
Calculation formula
Avoided CO2 emissions = CO2 reduction effect per wind turbine*1 x contribution rate*2
- "CO2 reduction effect per wind turbine" refers to the reduction that wind turbines using CFRP achieve over a power source mix (Carbon Fiber Sustainability Vision 2050, Japan Chemical Fibers Association)
- The number of wind turbines calculated from the sales volume of CHEMITYLEN used in CFRP for wind turbines. (Converted and calculated based on research data from market research companies and our market information)
Calculation formula
Avoided CO2 emissions = approx. 13 million t-CO2/year
CHEMITYLEN contributes in part to reducing CO2 emissions through the use of CFRP in wind power generation.